Development of a digital assistance system to reduce greenhouse gas emissions in industry
Motivation
Achieving carbon neutrality has become increasingly important for companies for a number of reasons. Increased sustainability demands from stakeholders and shareholders, rising energy and CO2 costs, and tightening policy frameworks are key drivers for focusing on the decarbonisation of business operations. The mandatory reduction of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions by 65% by 2030 compared to the base year of 1990 and the achievement of climate neutrality by 2045 underline the need for companies to quickly embark on a decarbonisation path.
The sequence of actions on this path to carbon neutrality is minimisation, substitution and offsetting. The core of corporate climate management, and the first step, is to improve the material and energy efficiency of companies. Every kilowatt hour that is not used does not emit greenhouse gases (GHG) and does not incur costs. This is where climate bOWL comes in.

Goals and projects
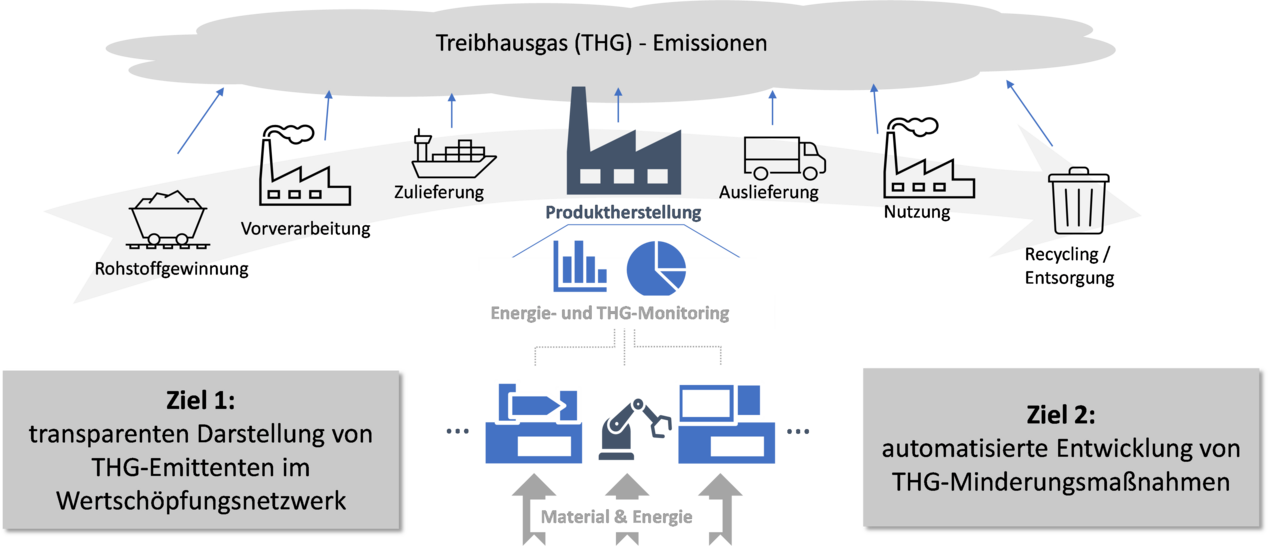
The overall objective of developing GHG reduction measures requires transparency of GHG along the value chain and is based on the interdisciplinarity of production, energy and information technology. Accordingly, a holistic approach to the aggregation and assessment of GHG is required to enable both the identification and prioritisation of GHG reduction measures.
The first sub-goal of the project is therefore to develop a product-specific carbon footprint tracking system that provides the required transparency through consistent, automatically validated and location-independent GHG data management.
Building on the tracking system, the second sub-goal is the automated development of climate protection and energy efficiency measures. To this end, an intelligent assistance system will be developed that uses energy and material flow data - supported by machine learning methods - to automatically allocate GHGs to their consumers, derive efficiency potential and determine the GHG avoidance potential.
Innovation
The GHG balance of the products and the reduction potential of each actor in the value chain are transferred to the Carbon Footprint Tracking System and aggregated. The innovation of the project is the transparent mapping of this information for each product and the actors involved. Currently, there is no transparent mapping of GHG in the horizontal value chain and the vertical production chain and no automated derivation of measures to reduce GHG. The development of the assistance system closes this gap and supports companies in the holistic development and evaluation of measures and roadmaps to achieve energy efficiency and climate targets.


